 For individuals living with diabetes, the feet can become vulnerable to a myriad of complications due to poor circulation and nerve damage. Left unchecked, these issues can escalate into non-healing wounds, infections, and even the risk of amputation. However, with proactive measures and timely interventions, many of these complications can be prevented or effectively managed.
For individuals living with diabetes, the feet can become vulnerable to a myriad of complications due to poor circulation and nerve damage. Left unchecked, these issues can escalate into non-healing wounds, infections, and even the risk of amputation. However, with proactive measures and timely interventions, many of these complications can be prevented or effectively managed.
This article delves into various aspects of foot care for diabetics, from preventive steps such as daily foot checks and routine podiatry evaluations to specific treatments for conditions like ingrown toenails, foot ulcers, diabetic neuropathy, and foot pain. Understanding and implementing these strategies can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals navigating the challenges of diabetes-related foot health concerns.
Ingrown Toenail Treatment
If you suffer from ingrown toenails, soaking your foot 3-4 times a day in warm water and rubbing an Epsom salt solution into the nail bed can help. This softens the ingrown toenail and reduces inflammation and pain. You can also trim your nails straight across rather than rounding them and wear shoes that fit properly to avoid the problem.
If a toenail becomes painful and infected, a podiatrist can help. Your clinician will numb your toe before removing the ingrown section of the nail. In severe cases, the nail matrix may be destroyed through surgical or chemical means (phenol matricectomy) to prevent it from growing back.
A simple way to prevent ingrown toenails is to elevate the lateral edge of your nail with a cotton wick that you can soak in disinfectant or antiseptic, and then place under the remainder of the nail. This eliminates the nail from digging in and piercing the skin, and will often bring immediate relief.
If the toenail is very painful and infected, a podiatrist like those in Talaria Podiatrist of Thornbury may need to remove part or all of your nails (visit their website at https://talariapodiatrist.com.au/ to learn more). Your doctor will numb your toe and then use scissors or other tools to remove the ingrown toenail. They will try to preserve the remaining parts of your nail to minimize recurrence. It can take 3-6 months for the toenail to regrow fully.
Foot Ulcers Treatment
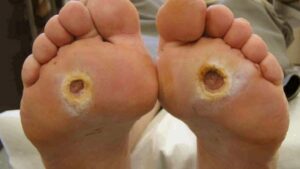
The damage caused by diabetes can make it hard to feel your feet, making them more likely to get injured. When an injury occurs, it may not heal properly, resulting in foot ulcers that can bleed and become infected. Left untreated, these ulcers can worsen and lead to amputation. Prompt treatment of a foot ulcer can prevent its progression and help you avoid lower-extremity amputation.
Your doctor cleans and disinfects the ulcer and removes dead tissue. Then, he or she may apply an antibiotic ointment to control infection and promote healing. He or she might also prescribe roomy, cushioned footwear and a brace or cast to take pressure off the ulcer area.
Depending on your symptoms, your doctor might order additional tests to check for blood flow problems in the legs and feet. These might include arterial Doppler ultrasounds and ankle-brachial pressure tests. Your doctor might also order imaging tests such as an X-ray or CT scan to visualize underlying bone damage underneath chronic wounds.
If your foot ulcer is infected, he or she might prescribe oral or IV antibiotics to control the infection. He or she might also perform a procedure called debridement to remove dead skin and speed up the healing process. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is another treatment option that can deliver more oxygen to your wound. Click here to know more about this process or talk directly to your local podiatrist.
Diabetic Neuropathy Treatment
Diabetes can reduce blood flow to the feet, damaging nerves and impacting sensation in the legs and feet. This is known as Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN). People with DPPN often experience pain, burning, or tingling in the feet. Symptoms are worse at night and can interfere with sleep and daily activities. DPN can also cause a loss of protective sensation in the foot, which can lead to untreated injuries and eventually result in ulcers or Charcot Neuroarthropathy (CN).
Those with diabetes should examine their feet regularly and seek medical help if they notice any changes to their feet. A GP or podiatrist will look at the skin, circulation, and sensation in the foot to determine whether DPN is present. They will ask about any other health problems and medications you may be taking. They will also check your reflexes and sensitivity to touch, vibration, and light.
You can improve your chances of preventing DPN by keeping your blood sugar levels under control, washing your feet daily, and using an emollient (like methylated spirits) to dry them, especially between your toes. Those with diabetes should also make sure they have a brisk walk daily to keep the blood flowing in their feet. You should also get your feet checked regularly to detect any signs of numbness or sores and ensure you treat any foot injuries promptly.
Foot Pain Treatment
Diabetes can cause poor circulation in the feet. Podiatrists will test a patient’s blood flow using tests like the monofilament or tuning fork tests in their podiatry clinic. This will determine if there is any damage to the small capillaries in the foot that could lead to serious complications.
Diabetes also causes nerve damage in the feet (diabetic neuropathy) that reduces sensation in the feet and toes. This can make it hard for a person with diabetes to notice that they have a cut or blister, which can then progress into an infection or non-healing ulcer. A podiatrist can teach a diabetic patient to inspect their feet daily, looking for any changes, cuts or bruises, red areas, and any signs of irritation, such as corns, calluses, and dry skin.
Diabetics are at high risk of developing a foot ulcer. If the wound does not heal, it may progress to a more serious infection that can result in amputation. A podiatrist can use a range of treatments including offloading techniques, antibiotics, and special shoes to help the wound heal. They can also help a diabetic patient prevent ulcers by educating them on proper foot care and frequent appointments with their podiatrist
Prioritizing foot care is paramount to preserving mobility and averting serious complications. By adopting preventive measures such as regular foot inspections and seeking prompt treatment for any abnormalities, individuals with diabetes can safeguard against the development of debilitating conditions like foot ulcers and neuropathy. Furthermore, accessing specialized care from podiatrists can offer targeted interventions tailored to individual needs, ensuring comprehensive management of foot health. With a proactive approach and collaborative efforts between patients and healthcare providers, it’s possible to mitigate the risks associated with diabetic foot complications and maintain optimal well-being.





